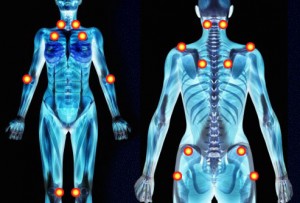
 Scientists estimate that over 6 million North Americans suffer from fibromyalgia, and experience widespread pain throughout their muscles and joints.
Scientists estimate that over 6 million North Americans suffer from fibromyalgia, and experience widespread pain throughout their muscles and joints.
Fibromyalgia symptoms include deep muscle pain, fatigue, tingling or numbness in hands and feet and painful trigger points. Additional symptoms can include anxiety, depression, difficulty concentrating, restless leg syndrome and TMJ.
Conditions that frequently overlap with fibromyalgia are severe headaches, chronic fatigue syndrome, myofascial pain syndrome, teeth grinding, allergies, and other autoimmune disorders.
The onset of fibromyalgia has been linked to traumatic events, such as accidents, certain diseases and long term or excessive stress.
The first step in treating fibromyalgia is to track your symptoms. Keeping track of your symptoms will help your health care practitioner to choose the best treatment option for you.
The next step is to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Reduce stress – limit overexertion and emotional stress
- Get enough sleep – establishing good sleep habits are essential
- Exercise regularly – appropriate exercises may include walking, swimming, and water aerobics
- Eat whole foods – eat healthy foods, limit caffeine and “stay-way” from sugary processed foods
The third step is to seek treatment from your health practitioners, and this can include:
Acupuncture: There is evidence suggesting acupuncture causes changes in blood flow and levels of neurotransmitters in the brain and spinal cord, and helps pain relief in fibromyalgia.
Massage therapy: Massage can relax your muscles, improve range of motion in your joints and increase production of your body’s natural painkillers, relieving stress.
eToims: If you are living with chronic pain, or fibromyalgia, there is a non-invasive treatment called Electrical Twitch Obtaining Intra-Muscular Stimulation, or “eToims” for short.
Class IV Laser: During each painless treatment laser energy increases circulation, drawing water, oxygen and nutrients to the damaged area. This creates an optimal healing environment that reduces inflammation, swelling muscle spasms, stiffness and pain. As the injured area returns to normal, function is restored and pain is relieved.
IMS/Dry needling: This treatment can greatly reduce tightness and pain, while increasing flexibility and range of motion. The needle sites target taut, painful muscle bands, and areas near the spine where the nerve root may have become irritated and super-sensitive.
Please contact our health care practitioners for more information on these treatment options for fibromyalgia.

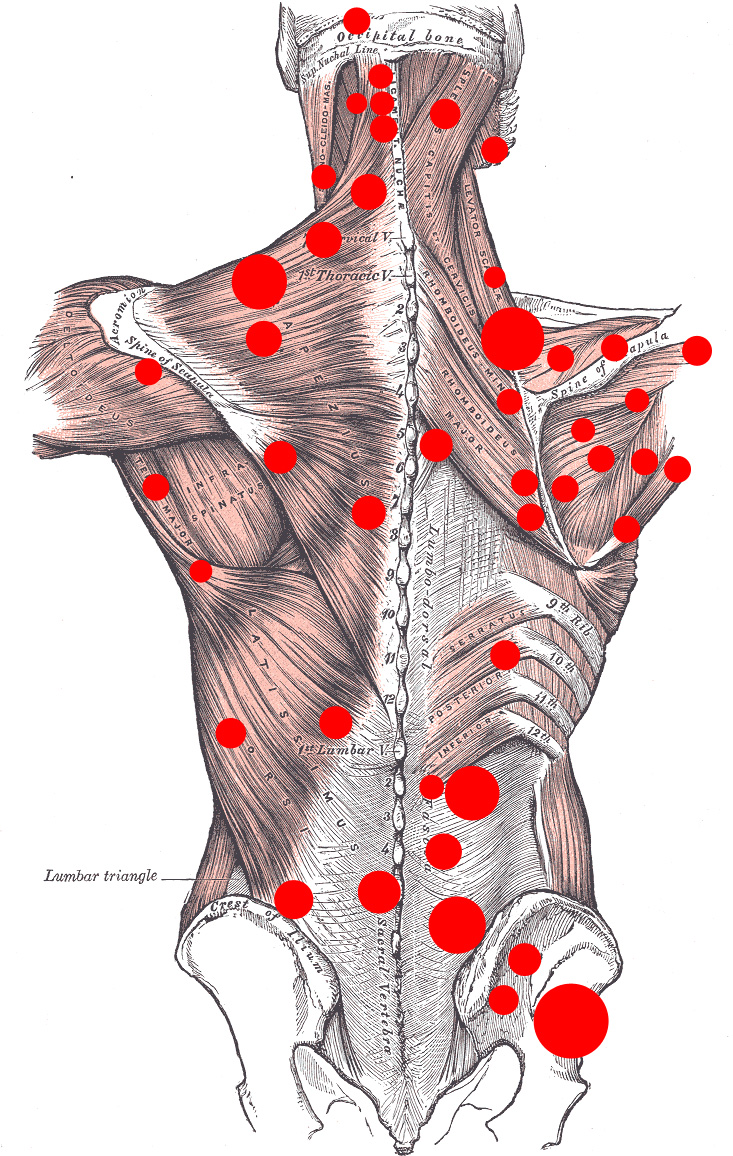 Myofascial pain syndrome is a chronic musculoskeletal pain disorder that can involve either a single muscle or a muscle group. It refers to pain and
Myofascial pain syndrome is a chronic musculoskeletal pain disorder that can involve either a single muscle or a muscle group. It refers to pain and Trigger point dry needling, also referred to as intramuscular stimulation (IMS) and/or intramuscular therapy (IMT) is an invasive procedure in which an acupuncture needle is inserted into the skin and muscle.
Trigger point dry needling, also referred to as intramuscular stimulation (IMS) and/or intramuscular therapy (IMT) is an invasive procedure in which an acupuncture needle is inserted into the skin and muscle. 