 Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. Older adults often get osteoarthritis, especially if they are overweight.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. Older adults often get osteoarthritis, especially if they are overweight.
Acupuncture, physical therapy or massage can help with osteoarthritis.
There are many helpful things you can do to ease the pain of osteoarthritis. Read on for some helpful advice.
What is osteoarthritis?
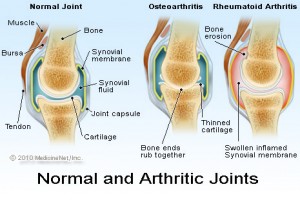
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects the cartilage that cushions your bones at the joints. Cartilage helps your bones glide over one another. If cartilage breaks down, the bones rub together. Osteoarthritis is a chronic (long lasting) condition.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis causes pain and stiffness in the joints. Osteoarthritis is often worst in the knees, hips and small hand joints. In most cases, the exact cause of osteoarthritis is not known.
Who is at risk of getting osteoarthritis?
- Women and men can both get osteoarthritis.
- Being overweight increases the risk of getting osteoarthritis. This happens because extra weight causes more wear and tear on the cartilage and joints.
- There are more cases of osteoarthritis in men who are younger than 45, while women tend to get it when they are 55 or older.
- Osteoarthritis can also occur due to repeated joint stress from certain physical jobs or sports.
- Osteoarthritis is genetic. That means you are more likely to get osteoarthritis if a family member also has it.
How can I manage OA?
Physical Activity
Start by being active. Physical activity is an important treatment, regardless of your age or level of pain. It can help:
- Reduce pain
- Maintain and improve joint movement
- Improve physical function
- Help you lose weight if you are overweight
Swimming is a good option since it puts no pressure on your joints. Activities that strengthen your muscles, such as weight lifting, are also important. Speak to your doctor or see a physical therapist before starting a physical activity program.
Weight management
Studies show that weight loss may help improve physical function for overweight or obese adults with osteoarthritis. Weight loss may also help ease pain.
Other treatments
- Some people find acupuncture, physical therapy or massage to be helpful.
- Applying heat and cold may also provide some pain relief.
- Severe cases of osteoarthritis may need surgery to replace or repair damaged joints.
Does a balanced diet help?
Healthy eating may help reduce the symptoms of different types of arthritis. Here are five healthy eating strategies:
1. Enjoy a wide variety of foods based on Canada’s Food Guide. This will provide the right balance of nutrients that your body needs.
2. Eat 7 to 10 servings of vegetables and fruits each day. Pick lots of bright orange and green options, such as broccoli, cantaloupe and carrots. They are high in antioxidants, which may reduce inflammation, decrease cartilage breakdown and slow the progress of osteoarthritis.
3. Choose more whole grains such as brown rice, barley and oats. They have more antioxidants than refined grains, such as white bread and white rice.
4. Choose more unsaturated fats like canola and olive oil, nuts like walnuts and almonds and fish like salmon.
5. Choose fewer foods made with saturated and trans fat like butter, lard, cream, baked goods and fried foods.
Are there medicines that can help?
Yes. Medicine can be used to reduce pain from osteoarthritis. Talk with your doctor about which medicines may be right for you. Your doctor may recommend:
- Pain relievers such as acetaminophen
- Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen if your pain continues
- Corticosteroids injected right into the joint to reduce swelling and pain
Speak to your health professional before starting any medicines for osteoarthritis so that he/she can help you pick what is right for you.
Are there supplements that can help?
Two supplements called glucosamine and chondroitin are thought to be helpful for osteoarthritis. However, they are not currently licensed for use as drugs to treat osteoarthritis because research does not show that they are effective. If you choose to try these products, make sure you buy ones that have a Natural Product Number (NPN). This means they are licensed with the Natural Health Products Directorate in Canada. Speak to your health professional before starting any supplements so that he/she can help you pick what is right for you.
Bottom line
If you have osteoarthritis, be active, enjoy a healthy eating plan and maintain a healthy weight. This can help ease the pain in your joints. Speak to your doctor before taking medicine for osteoarthritis.
This article was written by Dietitians of Canada.


 Diabetes is a chronic condition that stems from the body’s inability to sufficiently produce/properly use insulin which the body needs to use sugar as an energy source. Diabetes can lead to
Diabetes is a chronic condition that stems from the body’s inability to sufficiently produce/properly use insulin which the body needs to use sugar as an energy source. Diabetes can lead to  Victoria’s Diversified Health Clinic is the first location on Vancouver Island to offer
Victoria’s Diversified Health Clinic is the first location on Vancouver Island to offer  Written By Douglas Robb
Written By Douglas Robb The College of Family Physicians of Canada reports that 65% of all adults suffer from lack of
The College of Family Physicians of Canada reports that 65% of all adults suffer from lack of 
 The benefits of a good night’s sleep impacts every area of our daily life. While it may be obvious that sleep is beneficial, most people don’t realize how much sleep they need and why it is so important.
The benefits of a good night’s sleep impacts every area of our daily life. While it may be obvious that sleep is beneficial, most people don’t realize how much sleep they need and why it is so important.